Hepatitis A is a liver infection caused by a virus that is transmitted through contaminated water or food. It almost never has a fatal outcome and once healed you become immune. Let’s find out in detail its causes, symptoms, how to distinguish it from other forms of hepatitis and how to heal.
What is hepatitis
Hepatitis A is part of the hepatitis virus family, which literally means ‘inflammation of the liver’, an essential organ for our body. In fact, the functions it performs are fundamental:
- purifies the blood
- fights infections
- helps digestion
- stores nutrients, vitamins, and reserve energy
The various types of hepatitis a , b and c
The generic term of hepatitis is defined as a viral infection affecting the liver, derived from a family of 5 viruses. The most common types of hepatitis are:
- hepatitis A
- hepatitis B
- hepatitis C
Inflammation of the liver can also be caused by toxins, certain medications, alcohol consumption as well as bacterial infections and, as we have seen, viruses. The three most common forms of hepatitis are caused by three different viruses, have their own modes of transmission and can act on the liver in different ways.
Hepatitis A
It is the least severe of all viral hepatitis, and it does not become chronic. Usually, the body fights it within a few weeks, even without treatment, and the sufferer remains immunized for life.
The virus is transmitted through contaminated water, food, feces. This is why we must pay attention to raw or undercooked foods, and in particular to seafood from polluted areas. In general, it is a good idea to be careful especially in countries where there are poor hygienic conditions. Many here have already been infected with the virus and live there immunized. There is a vaccine , which protects especially in the case of immunosuppressed people.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is the most common and also the most dangerous type. The virus is transmitted through the blood or sperm of the infected person. Much more contagious than AIDS, however, it is treatable in almost all patients , only in 5% of cases it becomes chronic and the infected person becomes a ‘carrier’ of the virus and can transmit it to others.
While having no symptoms, there is a risk of developing liver cirrhosis or liver cancer, which are potentially fatal diseases. It can also be transmitted during childbirth.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is the most insidious form of viral hepatitis , because it is caused by a very resistant virus . Up to 80% of infections become chronic. Transmission occurs most often through direct contact with the blood of an infected person: mainly through exchange, reuse of non-sterile needles and syringes, and transfusion of untested blood.
More rarely it contracts during unprotected sexual intercourse with infected people. It is the leading cause of liver transplantation and unfortunately there is no vaccine to protect against it.
What is hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an infectious liver disease caused by the HAV virus: it is a highly contagious viral form that can sometimes resolve with a few weeks of treatment, sometimes it can remain severe for months. If the infection is mild, it heals completely and the liver is not damaged.
Spread of the virus
The virus is present all over the world, but above all in regions with poor hygiene standards, and little protection from sexual risks, due to a reduced culture of vaccines and prevention.
Approximately 1.4 million cases are estimated each year and children are predominantly affected.
Transmission hepatitis: how the virus is contracted
It is usually contracted by consuming food contaminated with the feces of an infected person. The hepatitis A virus is very contagious.
Transmission of the virus occurs more easily in countries where hepatitis A is common and in areas where there are poor sanitary conditions or poor personal hygiene.
Hepatitis A contagion
Contagion can occur due to:
- contact with feces: if a person does not wash their hands properly after changing diapers for example or having come in contact with the feces of an infected person;
- sexual intercourse with infected patients
- intake of food and drink or water contaminated with the virus (including frozen or undercooked food). The food and drinks most likely to be contaminated are fruits, vegetables, seafood, ice and water. In Italy the aqueduct distributes chlorinated water and this eliminates any chance of keeping the hepatitis A virus alive.
What are not risk factors
You are not infected with the hepatitis A virus:
- if you are next to a person with hepatitis A
- through coughing and sneezing
- through breastfeeding
How the diagnosis is made
If the doctor notices some typical symptoms, such as jaundice and increased liver volume during the palpation of the abdomen, he sends the patient to perform laboratory tests and in particular the blood test, the only one that allows to diagnose the disease.
In fact, the symptoms of hepatitis A are similar to those of other liver diseases which can be potentially serious.
Hepatitis A markers
The blood test includes looking for two antibodies to HAV , the virus responsible for hepatitis A:
- IgG value test that detects antibodies that appear as a result of the HAV virus, as a result of old infections or acquired immunity.
- IgM value test that detects early onset antibodies, which appear 5 to 10 days after exposure to the virus, peaking around 60-90 days after infection and persist for up to 6 months. Their presence indicates that the disease is ongoing.
Hepatitis A symptoms
Symptoms that should arouse suspicion include:
- tiredness
- pain in the abdomen, especially in the liver area, on the right side
- muscle and joint pain
- low-grade fever
- jaundice, which is yellowing of the skin and eyes
- nausea and vomiting
- loss of appetite
- itch
- dark urine
Hepatitis A incubation
Signs and symptoms therefore do not appear for more than a month after the virus was contracted. In some cases, especially among children, the symptoms do not appear and for this, unfortunately, they are able to transmit the virus.
The incubation period in healthy and adult people is 28 days . From the first symptoms of the infection to healing, it usually takes less than two months, but in some cases the symptoms can last up to six months.
In some individuals a mild form develops that it is asymptomatic .
What are the risk factors
There are situations that are considered risk factors for hepatitis A vision. Here are those:
- stay in countries with high rates of hepatitis A (they are all reported to the ASL)
- having sex with people who are infected or where the virus has become chronic (STD)
- live in contact with people affected by hepatitis A
- suffer from certain bleeding disorders, such as haemophilia
- using inept drugs , because you come into contact with infected syringes
- eat raw meat and fish of uncertain origin and preparation

Hepatitis A and diet
In addition to being infected by contact with someone who has been infected with the virus, the other main cause of the disease is nutrition . The foods most often at risk for hepatitis A are:
- non-mineral water
- seafood or raw or undercooked fish (watch out for sushi)
- raw fruit and vegetables badly washed or handled in poor hygienic conditions
- raw meat
- fresh unseasoned cold cuts (not raw ham)
- raw or lightly cooked eggs and derived sauces (mayonnaise, soft-boiled eggs)
- raw or unpasteurized milk (milk taken directly from the farmer)
- slightly aged soft cheeses made with raw milk
This virus is very resistant and is able to survive for months both in the stomach and in the first part of the intestine, despite this digestive tract being highly acidic. High temperatures, such as boiling, kill the virus, but not freezing. For this reason, frozen foods or chilled at -20 ° to solve the danger of anisakis are not safe from the point of view of the hepatitis A virus.
Hepatitis A in pregnancy
It is possible to contract hepatitis even during pregnancy , but the disease is usually benign and there is no risk to the fetus.
However, recent studies have shown that in some cases of infection in the second or third trimester, complications have then arisen, such as premature contractions, sudden placental abruption and premature rupture of membranes. Complications that led to premature labor, even if the evolution of the mother and the baby was favorable.
In this regard, vaccination can also be performed during pregnancy.
Hepatitis A children
Typical symptoms of hepatitis are common in children over 6 years of age and in adults, and a medical examination followed by a blood test will confirm the infection.
On the other hand, in children under 6 the disease goes unnoticed in most cases, even if the incubation lasts as in adults, from 15-30 days up to 50 days. The virus is present in the stool before clinical signs appear.
The treatments are the same as for adults, rehydration and rest, accompanied by a balanced and light diet.
Chronic hepatitis A
Unlike hepatitis B and C, A does not become chronic, and rarely has a fatal outcome, only if fulminant (with acute liver failure).
Once healed, antibodies develop that protect them for life. So the hepatitis A virus can only be caught once in a lifetime .
Hepatitis A cure
Those who contract this virus are usually able to recover completely without damage to the liver or liver functions. Infected people should still contact their doctor before taking any medication.
Usually, in a healthy adult man, the body gets rid of the virus on its own in a few weeks. It is therefore not necessary to hospitalize the patient except in the very rare case of an acute or fulminant form.
During the period when you are sick, the following treatment is recommended:
- absolute rest : one of the symptoms is profound tiredness. it is therefore advisable to stay in bed and rest a lot.
- Adequate Nutrition : Another common symptom is nausea which can make meals difficult. It is therefore advisable to eat light and easily digestible foods.
- drink plenty of fluids but avoid alcohol. The liver must be cleaned and left to rest. It is therefore advisable to limit any intake that can harm the liver such as too strong drugs, alcohol. Instead, drink plenty of water.
- avoid sexual intercourse. If you suffer from hepatitis, your doctor will recommend not having sexual intercourse because it is very contagious and even a condom does not guarantee total protection.
Prevention: Common Sense Tips
To avoid the risk of contracting hepatitis A, we recommend small gestures to be implemented in daily life:
- wash your hands well and often and dry them with disposable napkins
- if you are afraid of having the virus, do not prepare food for others : it is easily transmitted from hands to food
- do not use non-potable water even for making ice, washing or preparing food or kitchen utensils
- do not buy eggs that are too dirty with dirt or refrigerated: if the egg undergoes thermal changes, condensation may form on the shell, which favors the penetration of pathogenic germs
- wash fruit and vegetables before consuming them: for greater effectiveness, chlorine-based products can be used (bicarbonate is not enough). After soaking, rinse with clean, running water
- try to eliminate insects such as flies and cockroaches from the home, and protect food from contact with them, because they are a vehicle for pathogens
- using rubber gloves when carrying out small daily activities that lead to contact with material that could be contaminated – for example, cleaning cat litter boxes or gardening
- attention to cross-contamination , i.e. contact between raw products and ready-to-eat foods, between product and dirty utensils …
Permanent damage
It happens especially in the over fifties, or in people who already have other liver diseases, to be able to have more serious damage such as liver failure, which leads to the need for a liver transplant.
Fulminant hepatitis is very rare, but it can lead to death.
Post-exposure prophylaxis or Pep
The Pep or post-exposure prophylaxis is the attempt to prevent or cure a disease after an established exposure to the virus.
Hepatitis A vaccine
Certainly the safest method to prevent infection is the vaccine, consisting of the inactivated virus and is 94% effective. It is given in two doses six months apart intramuscularly, usually in the arm.
In this way the patient is immunized as early as 2-3 weeks after the injection of the first dose, and remains so for 10 years.
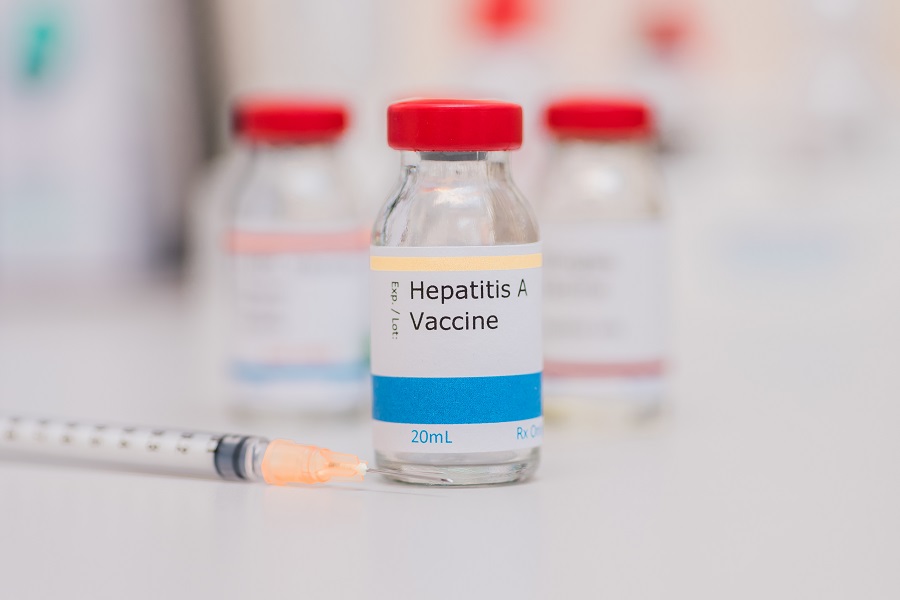
Hepatitis A vaccine: duration and hi vaccinate
Some countries also recommend vaccinating people at increased risk of hepatitis A, in particular:
- those who work in research laboratories and may come into contact with the virus
- travelers who intend to visit areas where the virus is endemic
- injectable drug users
- people with chronic liver disease, due to the increased risk of serious complications if they develop HAV
- children at the age of 1 year